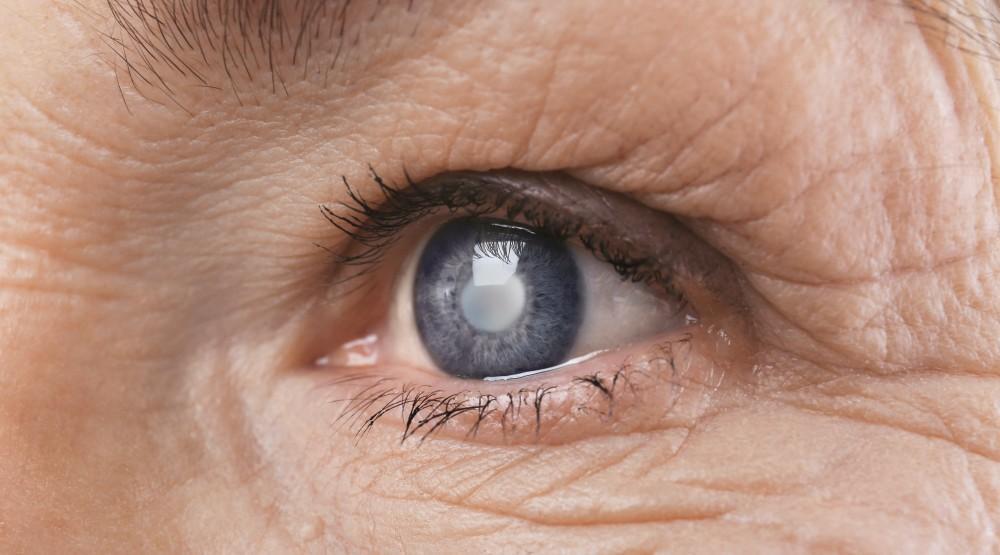
Cataracts are a common eye condition, particularly as we age, and they are one of the leading causes of vision loss worldwide. While the condition can sound daunting, cataracts are highly treatable, and modern advancements in eye care mean that most people can regain clear vision through surgery.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what cataracts are, their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and tips for prevention.
What Are Cataracts?
A cataract occurs when the clear lens of the eye becomes cloudy, making it difficult for light to pass through and focus on the retina. This leads to blurred or dimmed vision. Cataracts often develop gradually and are most commonly associated with ageing, but they can affect people of all ages.
What Causes Cataracts?
The lens of the eye is primarily made up of water and protein. Over time, changes in the arrangement of these proteins can cause the lens to become cloudy.
Key factors that contribute to cataract development include:
- Ageing: The most common cause, with cataracts often appearing after the age of 60.
- Exposure to UV Radiation: Prolonged sun exposure without eye protection can damage the lens.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can accelerate the formation of cataracts.
- Smoking: Chemicals in tobacco can damage the lens.
- Eye Injuries or Surgery: Trauma or previous eye surgery can lead to cataracts.
- Certain Medications: Prolonged use of corticosteroids is linked to an increased risk.
- Genetics: A family history of cataracts can raise your risk.
Symptoms of Cataracts
Cataracts typically develop slowly, and the symptoms may not be noticeable at first. As the condition progresses, you may experience:
- Blurred or cloudy vision.
- Sensitivity to light or glare, particularly at night.
- Difficulty seeing in low light or bright sunlight.
- Fading or yellowing of colours.
- Double vision in one eye.
- Frequent changes in your glasses or contact lens prescription.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to book an eye test with your optometrist for a thorough evaluation.
How Are Cataracts Diagnosed?
Cataracts are typically diagnosed during a comprehensive eye examination, which may include:
- Visual Acuity Test: To measure how well you can see at various distances.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: To examine the structures of your eye under magnification.
- Retinal Examination: To check for any abnormalities in the retina or optic nerve.
Treatment Options for Cataracts
1. Early-Stage Management
In the early stages of cataract development, symptoms can often be managed with:
- New glasses or stronger prescriptions.
- Anti-glare coatings for glasses to reduce sensitivity to light.
- Improved lighting for reading or other tasks.
2. Cataract Surgery
If cataracts significantly impair your vision and daily life, surgery is the most effective treatment. Cataract surgery is one of the most common and successful procedures performed in the UK.
- During surgery, the cloudy lens is removed and replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
- The procedure is typically done under local anaesthetic and takes about 30 minutes.
- Recovery is quick, and most people notice an improvement in their vision within a few days.
Preventing Cataracts
While some factors, like ageing, are unavoidable, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing cataracts:
- Protect Your Eyes from UV Rays
Wear sunglasses with UV protection and a wide-brimmed hat when outdoors. - Maintain a Healthy Diet
Eat foods rich in antioxidants, such as leafy greens, carrots, and citrus fruits. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish are also beneficial for eye health. - Manage Chronic Conditions
If you have diabetes or other health conditions, work with your doctor to keep them under control. - Quit Smoking
Smoking increases oxidative stress, which can damage the lens. Quitting reduces your risk of cataracts and other eye diseases. - Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol use can increase your risk of developing cataracts. - Have Regular Eye Tests
Routine eye examinations help detect cataracts and other eye conditions early, even before symptoms appear.
Cataracts and Driving in the UK
If you have cataracts, it’s crucial to ensure your vision meets the UK’s driving standards. If your vision falls below the legal requirement for driving, your optometrist or doctor will advise you to stop driving until your vision improves, typically after surgery.
When to See your Optometrist
If you experience sudden changes in your vision, significant glare, or difficulty performing daily tasks, book an appointment with an Optometrist. Early detection and treatment are key to maintaining your quality of life.
Final Thoughts
Cataracts are a common part of ageing, but they don’t have to lead to permanent vision loss. With regular eye tests, preventative measures, and access to advanced surgical options, you can maintain clear and healthy vision well into your later years.
If you’re concerned about cataracts or notice changes in your vision, contact your optometrist today for advice and support. Your vision is vital—prioritise its care!
Book a home test today
Fill in the form to request a home eye test, and one of our team will be in touch
If you have any questions, please call us on
Our other blogs